Diseases don’t affect humans alone but do affect other living organisms as well. Yes, even your poultry on your farm is not safe from diseases. They are also highly susceptible to several microorganisms like viruses and bacteria that lead to sickness. If you own a poultry farm, then you need to be cautious of poultry diseases.
When it comes to poultry diseases, Chickens are more likely to be affected by these diseases. And the reason is – chickens have a faster metabolism system than other pets, due to which diseases hit them too quickly. Most poultry diseases are caused by the invasion of a host by a pathogen that subsequently grows and multiplies in the body. More often than not, these diseases are contagious. This means they can be spread very quickly into the entire farm within no time at all.
If poultry diseases like Colibacillosis (one of the deadliest infectious diseases) are not detected on time, they can affect entire flocks. These diseases affect the immune system of the birds at once. Poultry diseases are of four types, namely; infectious diseases, metabolic and nutritional diseases, parasitic diseases, and behavioral diseases. However, there are some very severe and frequent diseases that every poultry owner should be aware of. Here in this post, we are sharing with you the five most common ailments along with their causes and symptoms.
Here we go….
1. Colibacillosis
At number one, we have Colibacillosis. It is highly infectious in nature and is one of the most common poultry diseases worldwide. It affects the respiratory system of the birds, thereby leading to septicemia and death.
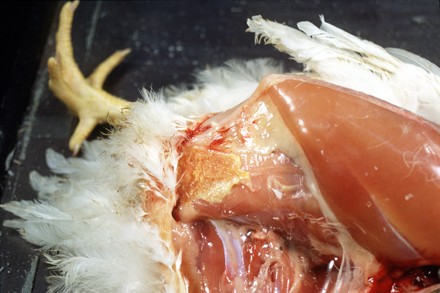
What Causes Colibacillosis?
This poultry disease is caused by the bacterium Escherichia coli, commonly known as E. coli. Strains of E. coli produce Colibacillosis. E. coli, which is found in the intestine of chickens, cause an infection under the skin, known as cellulitis. This can become so severe that the chickens can even die of this disease. One of its forms, ‘Avian Colibacillosis,’ affects broiler chickens between the age of 4 and 6 weeks. Once it spreads, it can lead to high mortality rates in a poultry farm.
Symptoms of Colibacillosis
The most common symptoms of Colibacillosis include respiratory distress, reduced appetite, runny noses, watery eyes, diarrhea, poor growth, and coughing in poultry. With these symptoms, you can easily detect the illness. Or else, the easiest way to detect this disease is to keep checking your flock and making sure they are energetic and do not have any disheveled feathers.
2. Newcastle Disease
Another highly contagious disease is Newcastle disease in poultry. Newcastle disease appears as a viral infection and is one of the most widespread illnesses found in chicken and other poultry birds. This disease affects the respiratory, gastro-intestinal, and the nervous systems of birds. If not detected on time, it can be severely fatal.
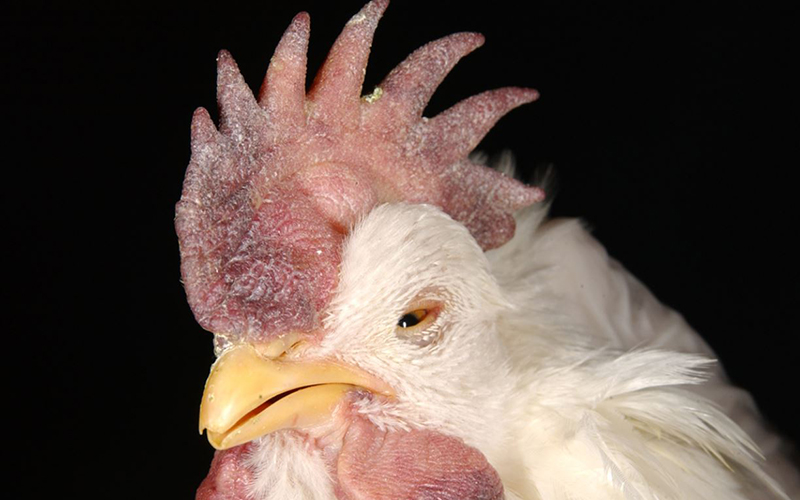

What Causes Newcastle Disease?
A virus, named Paramyxovirus cause Newcastle Disease. However, the pathogenicity of the infection varies from mild to highly pathogenic. Newcastle disease virus or NDV is usually spread by direct physical contact with infected or diseased birds. The NDV, which is present in manure, is breathed out into the air. Other sources of infection include contaminated water, food, equipment, and carcasses.
Symptoms of Newcastle Disease
The most common symptoms of Newcastle Disease include profuse diarrhea, drop in egg production rate, trouble breathing, depression, loss of appetite, and paralysis of the leg and wings. Another long-term nervous sign is a twisted neck, which usually happens when the bird survives. Newcastle disease spreads very rapidly. Hence, it is essential to contact the vet as soon as you detect these symptoms to avoid further damage to your poultry.
3. Chicken Anaemia Virus Infection
Chicken anemia virus infection or CAV is an acute viral infection found worldwide. This disease predominantly affects chickens. CAV can infect chickens of all ages; however, it is mostly detected in young chickens. CAV affects the immune system of the chicken, thereby leaving it more susceptible to other infections. Though the mortality is often a result of secondary infection.
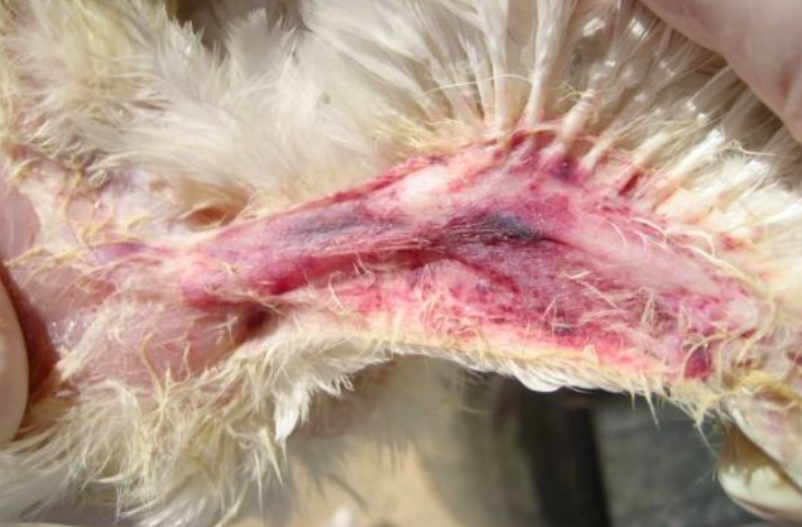
What Causes Chicken Anaemia Virus Infection?
CAV is caused by a virus called Chicken Anaemia Agent or CAA, a small DNA virus. Healthy chickens are less likely to this disease, while the ones with the weak immune system show higher susceptibility to disease. The virus can be spread from parents to offspring and birds to the entire flock. Infected birds tend to shed virus for up to 35 days. Roosters infected with CAV shed virus in their semen, while hens shed the virus into eggs during this viremic period.
Symptoms of Chicken Anaemia Virus Infection
The most common symptoms of CAV include anemia, depression, hemorrhage, inappetence, and a sudden rise in mortality. Chickens affected by CAV are highly likely to catch other infections, which eventually results in higher mortality rates.
4. Infectious Bursal Disease
Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD), also known by different names, such as Gumboro disease, infectious bursitis, and infectious avian nephrosis, is a highly contagious poultry disease. It generally affects young chickens and turkeys between the ages of 2 to 8 weeks. Usually, IBD is spread from infected chickens to healthy chickens, either directly or indirectly.

What Causes Infectious Bursal Disease?
Infectious Bursal Disease may appear suddenly, thereby resulting in 100% morbidity. It is caused by infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV). IBD is associated with bird age with the highest bursal mass. Young birds have between the ages of 2 to 8 weeks have highly active bursa of Fabricius. This is why they are more susceptible to infectious bursal disease. Birds over eight weeks are resistant to the virus and do not show any symptoms unless infected by highly virulent strains.
Symptoms of Infectious Bursal Disease
The most common symptoms of Infectious Bursal Disease include watery diarrhea, swollen feces-stained vent, ruffled feathers, high fever, trembling and slow walking, pecking at other chickens, yellow and foamy stool, difficulty in excretion, reduced appetite, and lying together in clumps with their heads sunken towards the ground. In the acute form, birds are debilitated, dehydrated, and prostrated.
5. Fowl Pox
Last but not least, another most common disease found in poultry is – Fowl Pox. Fowl Pox is highly contagious and should be closely monitored. It is comparatively a slow-spreading viral infection that affects most poultry bird species. This disease may occur at any time and to any age of the bird. Fowl Pox occurs in both a wet and dry form. The wet form is characterized by plaques in the mouth and upper respiratory tract. While the dry form is characterized by wart-like skin lesions that turn to thick scabs. Usually, fowlpox affects poultry’s appetite and egg production rate.
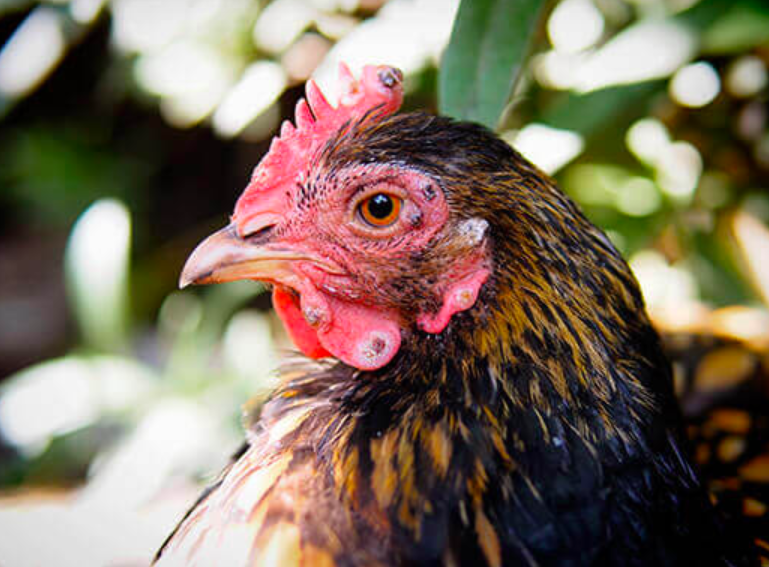

What Causes Fowl Pox?
Fowl pox is infectious in nature and is caused by an avian DNA pox virus. The infection primarily occurs through skin abrasions or bites, through the respiratory route, and ingestion of infective scabs. Fowlpox can be transmitted by birds, mosquitoes, and contaminated equipment. Poxvirus is highly resistant in dried scabs and can survive for months. Mosquitoes can harbor the Poxvirus for a month or more after feeding on infected birds and, in due course, can infect other birds as well.
Symptoms of Fowl Pox
The most common symptoms of Fowl Pox include reduced appetite, depression, poor growth, and reduced egg production rate. It takes up to three to five weeks for a bird to recover. To detect this disease, you should look out for these symptoms.
So, these are the five most common poultry diseases that each poultry owner should be aware of so that you can take timely action and prevent these diseases from spreading at a larger scale.
Ways to Prevent These Diseases.
The most surprising thing is – most poultry diseases have no treatment as such. The only prevention is through vaccination and by maintaining proper hygiene, sanitation, strict biosecurity, and procurement of birds from disease-free sources. As a poultry owner, you must get your poultry vaccinated for contagious diseases. Apart from this, have a vet regularly check your flock of chicken to ensure there are no symptoms of these diseases affecting your chicken. Needless to say, recovered birds are a reservoir of infection, make sure you remove them from the flock. Doing so will help you keep your flock of chicken in the best shape all the time and grow your poultry business.
Take the best care of your poultry so as to have the best results!!
